TSMC, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, is a semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company.
In part 1 of this TSMC analysis, we will be looking at the Growth of the industry and company; their current Dominance and trends as well as the Resilience of the company. Growth equates to companies growing to encroach on the market shares of other players while Resilience is the company’s ability to stop people from taking away their current market share and customers.
To be successful, the company will require both factors. As such, we need to analyse the Business component of TSMC to see if they have both.
TSMC’s Business
TSMC’s main business is centred in foundry, whereby they manufacture the semiconductor chips that are essential in the functioning of your electronic devices. Without these chips, your devices will not be able to work effectively[1]. However, they do not design the chips. Instead, they work to manufacture the specific designs drawn up by other companies like Apple, Nvidia and more.
Since TSMC is purely a manufacturer, they can easily gain the trust of major players in the tech space as they do not pose a threat of competition in terms of the production and selling of technological devices.
TSMC’S Growth
The current revenue growth of TSMC heavily supports the probability that the foundry segment’s revenue is likely to hit 10% annual growth in the future. This will create a 7% growth of the company as a whole and if you invest in TSMC, your investments could double easily in 7 years.
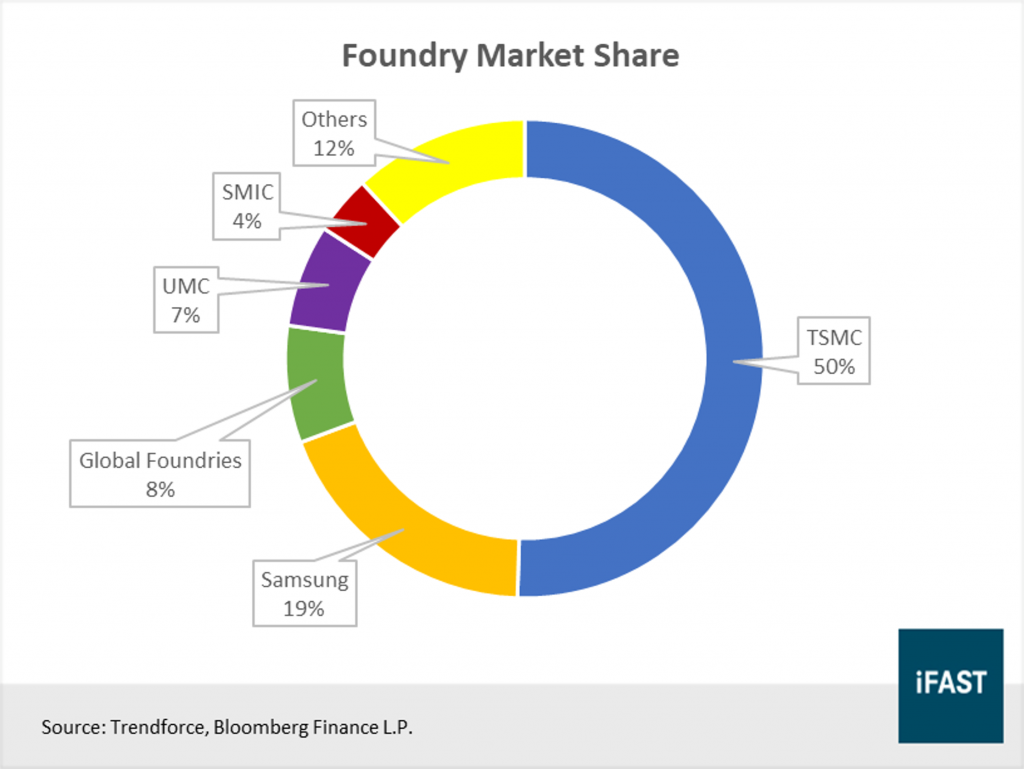
Looking at market share growth, we can see that as of the 3rd quarter of 2019, TSMC has obtained 50% of the market share amongst pure foundry companies. Samsung could be presumed to be a strong competitor, maintaining its ranking at 2nd place. However, Samsung is producing mainly for their own products and not for other companies like TSMC. Hence, the market shares are largely dependant on the sales of the other electronic goods it produces. Global Foundries stands at 3rd place but is currently losing money.
From the observations above, we know that TSMC is clearly a leader in this industry of semiconductor manufacturing. In fact, their market share is actually growing, and their competitors are dropping out.
Furthermore, semiconductor manufacturers are looking to double the number of transistors on the chip. This will allow users to save more power and enjoy faster processing. As such, there is always competition to make the chips smaller, with the world having reached the current size of 7 nanometre (nm, the size of a fuel cell) per semiconductor chip.
This has only been produced by 3 companies: TSMC, Samsung and Intel. However, we also must note that TSMC was the first to produce them in 2018 while Intel is yet to produce it and instead is predicted to produce it by 2021.
Close competitors like Intel can only produce the 7 nm chips by 2022 or 2023. As such, they are already 4 to 5 years behind TSMC and have a lot to catch up to. Intel is also looking at engaging a 3rd party to manufacturer these 7 nm chips as a contingency plan. This means that TSMC could be a customer to Intel instead of being a competitor. With the potential dropping out of a major competitor like Intel, the future of TSMC is even brighter and more specialised (being the only 2 producers of 7 nm chips).
Finally, we know that the semiconductor industry, and by proxy TSMC, will be growing as the demand for these chips will grow as it is necessary in all kinds of IT devices amidst this technological revolution.
TSMC’s Resilience
To protect against competitors encroaching on their market share, TSMC has several competitive advantages: Cost Advantage and Intangible Assets.
TSMC Cost Advantage
Looking at the cost of producing the chips, we can see that it takes $12 billion to build a plant, $5 million per equipment to create the chips and additional Research and Development (R&D) cost. If the company cannot produce enough, it is likely to lose money. Hence, even big companies like Global Foundries will experience losses. However, with such a large market share, TSMC can slowly offset the cost of production over selling a larger number of chips in comparison to any of its competitors.
The second competitive advantage is Intangible Assets like knowledge from R&D. Since the technology to produce smaller and smaller chips lie with the manufacturer, the learning to create these chips is incremental. Only by producing the 7 nm chip can they proceed easily to produce the 5 nm chip. As such, a major competitor like Global Foundries will have to content taking the lower margin of profit and lower technology in the market. While TSMC and Samsung will be able to capture the higher margin and prices in the market.
TSMC’s revenue: Is it recurring and diversified?
TSMC currently has only one business segment but the end demand of their segment is very diversified. TSMC produces chips for smart phones, AI and High Performance Computing. This means that TSMC is easily a part of multiple sunrise segments.
As of now, it is also hard to see the world finding an appropriate substitute for semiconductor chips. Hence, the risk that TSMC faces of being replaced is not very high.
In sum, TSMC is currently a major player in a lucrative industry. Furthermore, TSMC is ahead of their competitors in terms of advancement in R&D. Stay tune for part 2 by subscribing to the newsletter. We will look at more aspects of TSMC and draw a conclusion of whether it is a good investment opportunity then.
[1] If you want to read more about semiconductors, you can read: How semiconductors work
If you have any questions about your personal investment portfolio or want to learn how to better reap the opportunity you are now having, feel free to reach me via heb@thegreyrhino.sg or 8221 1200.
Remember to leave comments and share this site with your friends. Do subscribe to my newsletter for updates and share this site with your friends too. I would love to connect with you.

